BabelStone Blog
Sunday, 13 December 2009
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.0
A new and improved version of BabelPad that supports Unicode 5.2 has just been released, and can be downloaded directly by clicking here (simply unzip the file BabelPad.exe and run it from wherever you like). BabelPad will run on Windows 2000, XP, Vista and 7 systems, but I no longer provide a build that will run under Windows 95/98/Me (an unsupported build of Version 1.9.3 for Windows 95, 98 and Me is available at here for anyone who needs it).
This is the first official release of a new version of BabelPad since June 2008, and the first that to be announced here in over four years (BabelPad Version 1.9.3), because due to other commitments it has taken me nearly four years to get it into a fit state for release. As so many features have been added since the last official release, and as I have not yet got round to updating the help system, I think that it might be helpful to provide an overview of all the features and functions in the latest version of BabelPad.
Screenshot of BabelPad version 5.2.0 showing complex rendering with a virtual composite font
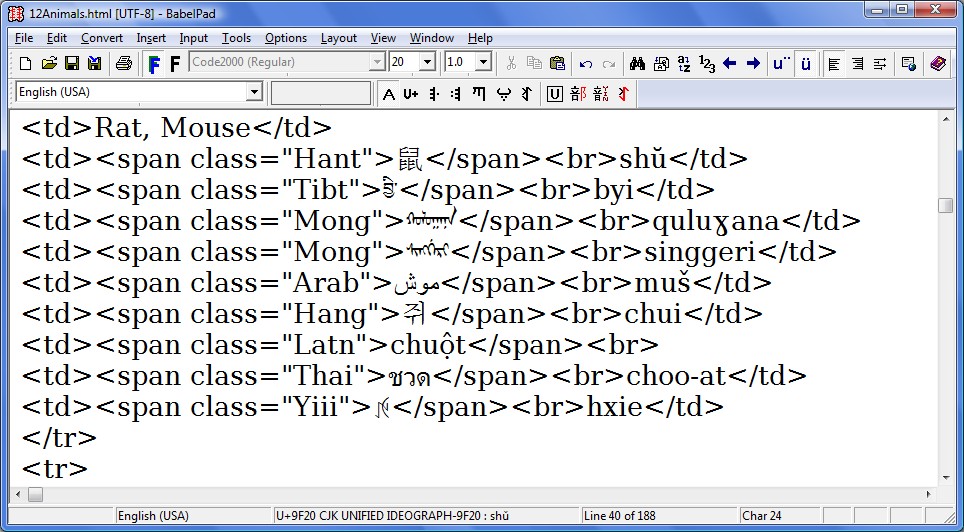
Click on the descriptions below to see different views of BabelPad
Complex rendering with a single font
Simple rendering with a virtual composite font
Complex rendering with a single font
Simple rendering with a single font
Complex rendering with a virtual composite font with colour highlighting of scripts
Browser view

All screenshots of BabelPad on this page are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License (CC-BY-SA-3.0) by Andrew West.
In summary, BabelPad is a plain text Unicode editor for Windows with standard text editing functionality (such as drag-and-drop editing, find/replace, and unlimited undo/redo of changes), as well as many enhanced features for working with multilingual and multiscript documents. As a "plain text" editor, you can edit the raw text that a document comprises, but you cannot apply styles such as Font, Font Size, Bold/Underline/Italics and Colour to arbitrary sections of text in the document. As a Unicode editor you can read, edit and write documents encoded in Unicode, and manipulate Unicode text at the character level (this is different from editors such as Notepad that allow you to edit at the Grapheme Cluster level). The code point value and character name of the character at the current caret position is indicated on the status bar, and pressing Ctrl+= brings up a summary of most of the defined properties of the character.
To ensure optimum display of a document you can either apply a single font to the entire document, or use a virtual composite font that maps different actual fonts to different Unicode blocks as configured by the user (font mapping is at the block level rather than the script level for various reasons, not least of which is that there are technical constraints that mean that it is currently impossible for a single font to individually cover all 75,000+ characters that are defined as belonging to the Han script). Unlike Notepad and other Windows applications, BabelPad does not perform any secret font substitutions that are outside the control of the user, and the font that is selected or configured will always be the font that is used to render the text. You can enable a single font as selected from a dropdown box on the main toolbar by pressing Ctrl+1, and enable the currently configured composite font by pressing Ctrl+2. Multiple composite fonts can be configured, and loaded as required.
By default BabelPad uses Microsoft's Uniscribe rendering engine to ensure complex scripts are rendered correctly, with appropriate joining and shaping behaviour where required, or for non-complex scripts where requested by OpenType features in the font (e.g. for ligatures of Latin letters). However, in order to visualize the underlying characters that the text comprises it is possible to turn off complex rendering, and display all characters as individual, spacing characters in logical order (e.g. Arabic characters will be displayed in their isolated forms, laid out left-to-right in Left-to-Right Layout or right-to-left in Right-to-Left Layout; and decomposed, accented Latin text will be laid out with individual diacritic marks following their base character in their coding sequence). You can enable simple rendering mode by pressing Ctrl+0 (Ctrl plus zero), and re-enable complex rendering mode by pressing Ctrl+9.
Below is a detailed list of features, ordered by menu position (yes I know, menus are out and ribbons are in, but personally I find a well-ordered menu system way more usable than a ribbon full of random icons).
File Menu
- New (Ctrl+N) : Closes the current document and creates a new, blank document. By design BabelPad has a single document interface, so if you want to work with multiple documents you need to open multiple instances of BabelPad. However, you can tile multiple instances of BabelPad using the Window menu options, which helps when working on two or more documents simultaneously.
- Open... (Ctrl+O) : Opens a new document. BabelPad can open documents encoded in a wide range of Uniocde and legacy encodings. By default BabelPad will auto-detect the document's encoding, which usually works for Unicode-encoded documents or for HTML/XML documents with a correct encoding declaration. The encoding that has been used to open the file )or later to save the file) is displayed in brackets after the file name on the title bar. With BabelPad it is possible to open and edit huge-sized text files (I recently opened the 230 MB UK database of post codes in about 40 seconds on my new laptop). Huge documents can be edited with little or no degradation in performance, but search operations may take a long time, and you should disable undo/redo if you want to make global changes to a very large document.
- Reopen As... : Reopens the current document with the option to select a different encoding, which is useful if you have inadvertently opened the docunent with the wrong encoding or if auto-detect gets the encoding wrong.
- Merge Files... : Allows you to select multiple documents (they must all be in the same folder) and open them as a single merged document.
- Save (Ctrl+A) : Saves the current document. If the document was opened as Read Only, or if it was not encoded as Unicode this will bring up the Save As dialog box. BabelPad can open documents in many different encoding, but by design it only saves documents in standard Unicode encodings (UTF-8, UTF-16 and UTF-32), or Unicode-compatible encodings (GB18030), or as ASCII text with non-ASCII characters represented using escape sequences or character entities.
- Save As... (Ctrl+Shift+S) : Save the current document with a new name, or in a different location, or with a different encoding. If you select a word or a short piece of text in the document (not going beyond a single line) and then Save As, the selected word or text (truncated to 64 characters) will be used as the default name for the document to be saved.
- Page Setup... : Sets the page size, orientation and margins to use for printing.
- Printer Setup... : Selects a printer to use for printing.
- Print... (Ctrl+P) : Prints the document.
- List of Recently Opened Files : Open (with auto-detect encoding) a recently opened document.
- Exit : Closes BabelPad.
Edit Menu
- Undo and Redo
- Undo (Ctrl+Z) : Undo the last edit action.
- Redo (Ctrl+Y) : Redo the last undone edit action.
- Undo All (Ctrl+Shift+Z) : Undo all edit actions made to the document.
- Redo All (Ctrl+Shift+Y) : Redo all undone edit actions to the document.
- Cut and Paste
- Cut (Ctrl+X) : Delete the selected text and copy it to the clipboard.
- Copy (Ctrl+C) : Copy the the selected text to the clipboard.
- Patse (Ctrl+V) : Paste any Unicode format or ASCII format text in the clipboard into the document at the current cursor position (replacing any selected text).
- Delete (Del) : Delete the selected text.
- Find and Replace
- Find... (Ctrl+F) : Opens the Find/Replace/Count dialog box with the Find button in focus (so that you can simply type a search term and hit Enter to start searching). You can make case-sensitive or case-insensitive searches (works for all Unicode characters with simple casing behaviour, including Armenian, Latin, Coptic, Cyrillic, Deseret, Georgian, Glagolitic and Greek letterss), and restrict matches by word boundary (whole word, start of word or end of word) or line boundary (whole line, start of line or end of line). Searching for a blank search term with the Whole Line option selected will find blank lines in the document.
- Find Next (F3) : Finds the next occurence in the document of the search term previously searched for (using the same search restrictions as previously used). If a piece of text not spanning more than one line is selected then the selected text will be used as a new search term, so in order to search for a particular word, all you need to do is simply double-click on it and hit F3.
- Find Next (unrestricted) : Same as Find Next, but does not apply any of the search restrictions (case matching and word/line boundary matching) that may have been used in the previous search.
- Find Previous (Shift+F3) : As for Find Next, but finds the previous occurence in the document of the search term previously searched for or the currently selected piece of text.
- Find Previous (unrestricted) : Same as Find Previous, but does not apply any of the search restrictions (case matching and word/line boundary matching) that may have been used in the previous search.
- Replace... (Ctrl+H) : Opens the Find/Replace/Count dialog box with the Replace All button in focus (so that you can simply type in a search term and replacement text and hit Enter to make a global replacement throughout the document or the selected text). If the Whole Line option selected with a blank search term, blank lines will be replaced by the replacement text; if the Start of Line option is selected with a blank search term, the replacement text will be prepended to the start of all lines in the document or in the selected lines of text; and if the End of Line option is selected with a blank search term, the replacement text will be appended to the end of all lines in the document or in the selected lines of text.
- Count... : Opens the Find/Replace/Count dialog box with the Count button in focus (so that you can simply type a search term and hit Enter to start counting). You may also count the occurences of a word or phrase by selecting the piece of text to be counted, and selecting Count from the right-click menu.
- Insert Lines... : Opens a dialog box that lets you enter the number of blank lines to insert at the current caret position.
- Join Lines... (Ctrl+J) : Opens a dialog box that lets you join together any two adjacent lines in the document where the first line ends with a given text string (if no text is given all lines will match) and the following line starts with a given text string (if no text is given all lines will match). If no text is given for the end of the first line text and for the start of the second line text then all lines in the document (or the selected lines of the document) will be joined into one long line.
- Break Lines... (Ctrl+K) : Opens a dialog box that lets you insert one or more line breaks into all occurences of a given text string (type a circumflex character at all required line break positions).
- Replicate Character (Ctrl+R) : Reduplicates the character before the caret.
- Reverse : Reverses the selected text at the grapheme cluster level (i.e. a decompsed sequence of a base letter and one or more diacritic marks will be treated as a single unit).
- Transcode... : Opens a dialog box that allows you to perform a custom transcoding of the document, i.e. convert all occurences of characters in usr-defined List A to the corresponding character in user-defined List B. This feature could be useful when working with legacy or PUA encoded documents, as well as for encoding or deciphering a substitution cipher.
- Auto Number... : Opems a dialog box that allows you to convert all occurences of "###" (triple hash) in the doument to numbers, starting from a given number and incrementing/decrementing by a given number, either in decimal or hexadecimal. For example, to add line numbering to a document, first replace the start of every line with "###" (use a blank search term and Start of Line checked), then open the Auto Number dialog box and hit Enter (using the default values).
- Increase Indent (Tab) : Adds a tab character to the start of each selected line (a whole number of lines must be selected).
- Decrease Indent (Shift+Tab) : Removes a tab character from the start of each selected line.
- Select All (Ctrl+A) : Selects the entire document.
- Go To... (Ctrl+G) : Opens a dialog box that allows you to enter a logical line number to go to.
- Screenshot of BabelPad : Copies an image of the entire BabelPad window to the clipboard (for unknown reasons this may not always work correctly on Vista and 7).
- Screenshot of Edit Pane : Copies an image of the BabelPad edit pane to the clipboard.
Convert Menu
- Contextual Convert... (Ctrl+Shift+X) : Opens a dialog box that allows you to apply any of the other conversions on the conversion menu (casing, normalization, etc.) to only that text that occurs between two user-defined delimiters. For example, you could use this feature to convert to upper case all text that occurs between <h1> and </h1>. Or you could convert from Wylie Transliteration to Unicode Tibetan all text that occurs between lang="bo"> and </.
- Case
- To Upper Case (Ctrl+U) : Converts the selected text to upper case.
- To Lower Case (Ctrl+L) : Converts the selected text to lower case.
- To Title Case (Ctrl+T) : Converts the selected text to upper case at word-start and to lower case elsewhere.
- Normalization Form
- To NFD : Converts the selected text to Normalization Form D (i.e. canonical decomposition of the text).
- To NFC : Converts the selected text to Normalization Form C (i.e. canonical decomposition of the text followed by recomposition of all decomposed sequences).
- To NFKD : Converts the selected text to Normalization Form KD (i.e. compatibility decomposition of the text).
- To NFKC : Converts the selected text to Normalization Form KC (i.e. compatibility decomposition of the text followed by recomposition of all decomposed sequences).
- HTML Entities
- HTML Entities to Unicode : Converts all occurences of HTML character entity references (e.g. é for é) in the selected text to their corresponding Unicode characater.
- Unicode to HTML Entities : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to their corresponding HTML character entity reference where possible.
- Numeric Character References (NCR)
- NCR to Unicode : Converts all occurences of numeric character reference in either decimal format (e.g. ꯍ) or hexadecimal format (e.g. ꯍ) in the selected text to their corresponding Unicode character.
- Unicode to NCR (Hex) : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to their corresponding hexadecimal format numeric character reference where possible.
- Unicode to NCR (Decimal) : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to their corresponding decimal format numeric character reference where possible.
- Universal Character Names (UCN)
- UCN to Unicode : Converts all occurences of Unicode character name escape codes (e.g. \uABCD; or \U00013055) in the selected text to their corresponding Unicode character.
- Unicode to UCN : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to their corresponding universal character name where possible.
- To Unicode Name : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to their official Unicode name (e.g. U+ABCD converts to MEETEI MAYEK LETTER HUK).
- To U+XXXX : Converts all occurences of Unicode characters outside the Basic Latin block in the selected text to the U+XXXX notation (e.g. U+ABCD or U+13055).
- Chinese
- To Traditional Characters (Ctrl+Shift+F) : Converts all occurences of simplified Chinese characters in the selected text to the appropriate corresponding traditional character, based on context (e.g. 干净 converts to 乾淨, but 能干 converts to 能幹).
- To Simplified Characters (Ctrl+Shift+J) : Converts all occurences of traditional Chinese characters in the selected text to the appropriate corresponding simplified character, based on context (e.g. 乾淨 converts to 干净, but 乾坤 remains as 乾坤).
- HKSCS PUA Ideographs : Converts all occurences of Private Use characters defined in the Hong Kong Special Character Set (HKSCS) in the selected text to their corresponding Unicode character.
- Japanese
- Hiragana to Katakana : Converts all occurences of Hiragana characters (3040..309F) in the selected text to the corresponding Katakana character.
- Katakana to Hiragana : Converts all occurences of Katakana characters (30A0..30FF) in the selected text to the corresponding Hiragana character.
- Korean
- Hangul Syllables to Hangul Letters : Converts all occurences of precomposed Hangul syllables (AC00..D7A3) or decomposed Hangul Jamo (1100..11FF) sequences in the selected text to the corresponding spacing Hangul letters (3131..318E).
- Hangul Letters to Hangul Syllables : Converts all occurences of spacing Hangul letters (3131..318E) in the selected text to the corresponding precomposed Hangul syllables (AC00..D7A3) or decomposed Hangul Jamo (1100..11FF) sequences.
- Tibetan
- Extended Wylie to Tibetan : Converts Tibetan transliteration (Extended Wylie Transliteration Scheme) to Unicode Tibetan.
- Unicode to Precomposed Tibetan (Set A) : Converts standard Unicode Tibetan text to the Private Use precomposed Tibetan Set A characters defined by the PRC.
- Precomposed Tibetan (Set A) to Unicode : Converts Private Use precomposed Tibetan Set A characters to standard Unicode Tibetan.
- Uyghur
- Arabic to Latin (ULY) : Converts Uyghur text written in Arabic characters to the Uyghur Latin Yéziqi (ULY) orthography.
- Latin (ULY) to Arabic : Converts Uyghur text written in the Uyghur Latin Yéziqi (ULY) orthography to Arabic characters.
- Vietnamese
- VIQR to Unicode : Converts Vietnames text written in Vietnamese Quoted-Readable (VIQR) to standard Unicode Vietnamese.
- Unicode to VIQR : Converts standard Unicode Vietnamese to Vietnamese Quoted-Readable (VIQR).
- Yi (Nuosu)
- Yi Romanization to Yi Syllables : Converts Nuosu Yi text written in Romanization to Yi syllables (A000..A48C).
- Yi Syllables to Romanization : Converts Nuosu Yi text written in Yi syllables (A000..A48C) to Romanization.
- Yi Syllables to IPA : Converts Nuosu Yi text written in Yi syllables (A000..A48C) to IPA transcription.
- Other
- Fullwidth and Halfwidth to Normal Width : Converts all occurences of fullwidth and halfwidth Latin, Katakana and Hangul letters (FF00..FFEF) in the selected text to the corresponding normal width characters.
- Control Codes to Control Pictures : Converts all occurences of control characters (0000..001F and 007F) in the selected text to the corresponding control picture (2400..243F).
- ASCII to Tag Characters : Converts all occurences of Basic Latin characters (0020..007E) in the selected text to the corresponding tag characters (E0000..E007F).
- ASCII to Typographic Characters : Converts ASCII apostrophe and quotation mark to opening/closing single and double quotation marks as appropriate, converts two consecutive ASCII hyohen-minus characters to an em dash, and converts occurences of number-slash-number to the corresponding fraction characters.
- Strip Diacritics : Removes diacritic marks from all occurences of letters with diacritic marks in the selected text.
Insert Menu
- File... : Opens a File Open dialog box in order to select a file to insert into the document at the current caret position. This operation cannot be undone, and clears any existing undo operations.
- Bidirectional Control Characters : Inserts a bidirectional control charater (LRM, RLM, LRE, RLE, LRO, RLO, PDF) into the document at the current caret position.
- Interlinear Annotation Control Characters : Inserts an interlinear annotation control charater (interlinear annotation anchor/separator/terminator) into the document at the current caret position.
- Deprecated Format Characters : Inserts a deprecated format charater (ISS, ASS, IAFS, AAFS, NADS, NODS) into the document at the current caret position.
- Zero Width Joiner (ZWJ) (Alt+=) : Inserts a Zero Width Joiner charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Zero Width Non-Joiner (ZWNJ) (Alt+Shift+=) : Inserts a Zero Width Non-Joiner charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Combining Grapheme Joiner (CGJ) : Inserts a Combining Grapheme Joiner charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Word Joiner (WJ) : Inserts a Word Joiner charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Object Replacement Character : Inserts an object replacement charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Replacement Character : Inserts a replacement charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Variation Selectors : Inserts a variation selector charater into the document at the current caret position.
- Spaces : Inserts one of a variety of space charaters into the document at the current caret position.
- Dashes and Hyphens : Inserts one of a variety of dash and hyphen charaters into the document at the current caret position.
Input Menu
- Default (Ctrl+D) : Uses the currently selected Windows keyboard layout or input method for text input.
- Unicode (Ctrl+I) : Uses the BabelStone Unicode input method to enter Unicode characters by scalar value. Enter any Unicode character by typing its Unicode code point value terminated by hitting the space key or the Enter key. You can also enter a single Unicode character in any other input mode by hitting Ctrl+Q followed by the code point value of the character terminated by space or Enter.
- Manchu (Ctrl+Shift+A) : Uses the BabelStone Manchu phonetic input method to enter Manchu text.
- Mongolian (Ctrl+Shift+M) : Uses the BabelStone Mongolian phonetic input method to enter Mongolian text.
- Tibetan (Ctrl+Shift+B) : Uses the BabelStone Tibetan Extended Wylie input method to enter Tibetan text.
- Uyghur (Ctrl+Shift+U) : Uses the BabelStone Uyghur input method to enter Uyghur text (this is the same as the Microsoft Uighur keyboard layout for Vista, except that it maps F to U+0641 ARABIC LETTER FEH rather than U+06A7 ARABIC LETTER QAF WITH DOT ABOVE as Microsoft incorrectly does).
- Yi (Nuosu) (Ctrl+Shift+N) : Uses the BabelStone Yi romanization input method to enter Nuosu Yi text.
Tools Menu
- Character Map... (Ctrl+M) : Opens the character map tool that allows you to select any Unicode character. This is a simplified version of the BabelMap application.
- Advanced Character Search... : Opens the Advanced Character Search tool that allows you to search for all characters that match certain criteria (for example, a particular formal property of the character or the version of Unicode that the character was introduced in).
- Document Analysis... (F7) : Opens the Document Analysis tool that provides statistics for the current document, and reports any warnings or errors.
- Character Frequency... : Opens the Character Frequency tool that lists the frequency of all characters in the document (useful for deciphering substitution ciphers).
- Font Analysis... : Opens the Font Analysis tool that lists the character coverage of all fonts in the system.
- Font Coverage... : Opens the Font Coverage tool that allows you to list all fonts that cover a particular character, or a given piece of text, or all the characters in the current document.
- Font Information... : Opens the Font Information tool that shows information about the currently selected font.
- Export Font Glyphs... : Opens the Font Glyph Export tool that allows you to save to file in BMP, GIF, JPG or PNG format any glyphs from a given font (selected by code point value or glyph index).
- Unicode Summary... : Opens the Unicode Summary tool that provides a summary of the planes, blocks and scripts defined in the current version of Unicode.
- Unicode Version History... : Opens the Unicode Version History tool that provides summary details about each version of Unicode.
- Mandarin (Pinyin) Lookup... (F12) : Opens the Mandarin Lookup tool that allows you to find a Chinese character by Pinyin pronunciation.
- Cantonese (Jyutping) Lookup... (Shift+F12) : Opens the Cantonese Lookup tool that allows you to find a Chinese character by Jyutping pronunciation.
- Han Radical Lookup... (F11) : Opens the Han Radical Lookup tool that allows you to find by radical and residual stroke count any of the 74,394 characters in the CJK, CJK-A, CJK-B and CJK-C blocks.
- Yi Radical Lookup... (Shift+F11) : Opens the Yi Radical Lookup tool that allows you to find any Yi syllable by radical and residual stroke.
- Character Properties... (Ctrl+=) : Opens the Character Properties dialog box that shows additional information about the character at the current caret position.
Options Menu
- Single Font (Ctrl+1) : Renders the document with a single font (as selected from the dropdown list on the main toolbar).
- Composite Font (Ctrl+2) : Renders the document using a user-defined composite font, with a font mapping for each Unicode block of characters.
- Simple Rendering (Ctrl+0) : Renders text as spacing characters in logical order with no shaping or joining behaviour, and with format characters displayed with visible glyphs if available in the font.
- Complex Rendering (Ctrl+9) : Renders text using Microsoft's Uniscribe rendering engine, which normally gives the best shaping and joining behaviour for complex scripts (BabelPad accesses the Uniscribe API directly, so avoids automatic font substitution and other potentially unwanted behaviour found in Notepad, etc.).
- User Interface Language : Changes the language used for menus and other user interface items. Currently only supports English, Simplified Chinese and Traditional Chinese.
- CJK Readings : Selects which language to display readings of Han ideographs in on the main status bar and on the character map status bar. Available languages are Mandarin (pinyin), Cantonese (jyutping), Korean and Vietnamese.
- Dialogue Boxes : Allows you to select whether to display small-sized or medium-sized dialog boxes (if your system has a small screen resolution small-sized is best).
- Display Colours : Selects the text and background colours for the main edit pane : default system colours; black text on white background; white text on blue background; or each Unicode-defined script displayed in a different colour.
- Font Options
- List Unicode Fonts Only : By default BabelPad lists all TrueType and OpenType fonts, even those that have no Unicode character-to-glyph mapping, and so are not fully supported by BabelPad. Checking this option will cause any such fonts to be filtered out of the font list.
- List Rotated Fonts : By default BabelPad does not list vertical forms of CJK fonts. Checking this option causes BabelPad to include in the font list vertical versions of fonts where available (i.e. fonts that appear with an @ sign in front of their names).
- List All Styles of Fonts : By default BabelPad only lists the regular style of fonts with more than one sttyle. Checking this option causes BabelPad to list all available styles of each font (e.g. Bold, Italic, Bold-Italic).
- File Options
- Save New Files with a BOM : Selects whether to save new files with a Byte Order Mark (BOM) or not. For existing files, the default is to save with a BOM if the file had one when it was opened, and without a BOM if it did not have one when it was opened.
- Set Maximum Line Size... : BabelPad's one weakness is that it does not cope with very long lines very well. If you are having problems with documents with very long lines, you can use this option to soecify a maximum line size, and when opening files BabelPad will automatically insert one or more line breaks in any lines that are longer.
- Edit Options
- Enable Undo/Redo : If you are making global changes to a very large document you should disable the undo/redo functionality, otherwise text replace and conversion operations make take an excessively long time.
- Enable Auto-Indent : If this option is selected tab character will be automatically inserted at the start of a new line when Enter is entered if required (mainly intended for C/C+/C# code editing, but also useful for editing XML documents).
- Enable Smart Quotes : If this option is selected ASCII apostrophe and quotation marks will be automatically converted to opening or closing single/double quotation marks as necessary, as you type (press Ctrl-Z to revert to the original character typed).
- Enable Smart Fractions : If this option is selected ASCII sequences of a digit followed by a slash followed by a digit (e.g. 3/4) will be automatically converted to the corresponding fraction character (e.g. ¾) as you type (press Ctrl-Z to revert to the original sequence of characters typed).
- Enable Smart Dashes : If this option is selected two consecutive ASCII hyphen-minus characters will be automatically converted to an em dash character as you type (press Ctrl-Z to revert to the original characters typed).
- Convert Basic Latin : By default the various conversions of Unicode characters to escape codes or character entities (NCR, UCN, U+XXXX, etc.) are only applied to characters beyond the Basic Latin block (0000..007F). If this option is selected, all characters will be subject to such conversion operations.
- Casing Rules
- Turkish/Azeri (dotted/dotless i) : Checking this option will apply Turkish /Azeri casing rules for dotted i and dotless i when performing casing operations to text.
- Lithuanian (accented dotted i/j) : Checking this option will apply Lithuanian rules for preserving the dot on accented lower case i and j when performing casing operations to text.
- German (eszett) : Allows you to choose which rules to use for casing eszett (ß) and SS : None (eszett is uppercased to SS,but SS is never lowercased to eszett); Traditional (eszett is uppercased to SS, and medial/final SS is lower cased to eszett); or modern (eszett is uppercased to capital eszett, and capital eszett is lowercased to eszett).
- Long S : Allows you to choose which rules to use for lowercasing capital S to short s or long s when converting upper case text to to lower case : None, Early 18th Century English rules; Late 18th Century English rules; 18th Century French rules; 18th Century Italian rules; or 18th Century Spanish rules.
- Other Options
- Help Window on Top : As recommended by Microsoft, by default the Help window is always on top of the BabelPad window. If you find this annoying, select this option.
- Composite Font Mappings... : Opens a dialog box that allows you to configure which Unicode blocks are mapped to which fonts in the virtual composite font. Multiple virtual composite fonts can be defined and saved to file.
Layout Menu
- Left to Right Layout (Ctrl+Shift+L) : Lays out the document in Left-to-Right page layout.
- Right to Left Layout (Ctrl+Shift+R) : Lays out the document in Right-to-Left page layout.
- Line Wrap (Ctrl+W) : Toggles between Line Wrap and No Line Wrap mode.
View Menu
- Main Toolbar : Shows or hides the toolbar with buttons corresponding to the most common file, editing and display options, including a dropdown list of fonts on the system.
- Input Toolbar : Shows or hides the toolbar with buttons corresponding to the BabelStone input methods and character lookup tools.
- Convert Toolbar : Shows or hides the toolbar with buttons corresponding to general conversion functions.
- Language Toolbar : Shows or hides the toolbar that has buttons corresponding to various language-specific functions.
- Options Toolbar : Shows or hides the toolbar with buttons corresponding to common options.
- Status Bar : Shows or hides the status bar. The status bar shows informational messages, the current keybaord layout or input method, the code point value and official character name of the character at the current caret position (as well as the Mandarin, Cantonese, Korean or Vietnamese reading for CJK ideographs), the current line number and the character position on the current line.
- Edit View (Ctrl+E) : Exits Browser mode and re-enters Edit mode.
- Browser View (Ctrl+B) : Enters Browser mode, where the current document is displayed in an Internet Exporer window.
Window Menu
- Tile Windows : Tiles in an orderly fashion all non-minimized BabelPad windows.
- Tile Horizontal : Tiles horizontally (left to right across the screen) all non-minimized BabelPad windows.
- Tile Vertical : Tiles vertically (top to bottom down the screen) all non-minimized BabelPad windows.
- Tile across all Monitors : Tiles all non-minimized BabelPad windows across all monitors attched to the system (the above three options only tile across a single monitor).
- Cascade Windows : Cascades all non-minimized BabelPad windows.
- Minimize Windows : Minimizes all instances of BabelPad.
- Maximize Windows : Maximizes all instances of BabelPad.
- Restore Windows : Restores all instances of BabelPad.
- Close Windows : Closes all instances of BabelPad.
Help Menu
- Help Topics (F1) : Opens the Help system (currently not up to date).
- About BabelPad... : Opens a dialog box showing information about the current version of BabelPad.
Mouse Click Functions
- Left Click on Margin (left margin in LTR mode or right margin in RTL mode) : selects the adjacent physical line
- Double Left Click on Margin (left margin in LTR mode or right margin in RTL mode) : selects the adjacent logical line (i.e. one or more physical lines in Line Wrap mode)
- Right Click on Text : brings up a small menu with common edit and convert operations.
Mouse Scroll Wheel Functions
The mouse scroll wheel has the following functions that can be used to manipulate the dropdown lists (Font, Font Size and Line Spacing) on the main toolbar, even when the main toolbar is hidden :
- Scroll : scrolls the text in the edit pane
- Shift+Scroll : scrolls through the dropdown list of fonts if not using a composite font
- Ctrl+Scroll : increases or decreases the font size
- Ctrl+Shift+Scroll : increases or decreases the line spacing
Keystroke Navigation
The following keystroke combinations may be used to move the current caret position within a document (holding the Shift key down at the same time will select the text between the start and end caret positions) :
- Home : moves the caret to the start of the current physical line (i.e. to the beginning of a wrapped line in line wrap mode)
- Home+Home (in quick succession) : moves the caret to the start of the current logical line (i.e. in front of the first character of a logical line that spans several physical lines when in Line Wrap mode)
- End : moves the caret to the end of the current physical line (i.e. to the end of a wrapped line in line wrap mode)
- End+End (in quick succession) : moves the caret to the end of the current logical line (i.e. after the last character of a logical line that spans several physical lines when in Line Wrap mode)
- Left : moves the caret one Unicode character to the left
- Right : moves the caret one Unicode character to the right
- Up : moves the caret to the same relative position in the physical line above (relative to the start of the physical line)
- Down : moves the caret to the same relative position in the physical line below (relative to the start of the physical line)
- Ctrl+Home : moves the caret to the start of the document
- Ctrl+End : moves the caret to the end of the document
- Ctrl+Left : moves the caret to the start of the previous word
- Ctrl+Right : moves the caret to the start of the next word
- Ctrl+Up : moves the caret to the same absolute position in the logical line above (relative to the start of the logical line)
- Ctrl+Down : moves the caret to the same absolute position in the logical line below (relative to the start of the logical line)
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.1 [2009-12-14]
This update fixes a bug in the menu display that affects US English users only.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.2 [2009-12-16]
This update has the following improvements and bug fixes:
- Improves behaviour when pasting text or inserting a file.
- Improves behaviour when selecting all text (Ctrl+A) and not in Line Wrap mode.
- Fixes a bug that caused the horizontal scrollbar to not always be shown after exiting Line Wrap mode.
- Improves Manchu input method (allows 'tsy' sequence and maps plus sign (+) to the syllable boundary marker).
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.3 [2009-12-21]
This update fixes two bugs in the Uyghur "Latin (ULY) to Arabic" conversion function.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.4 [2009-12-23]
This update fixes a bug that causes BabelPad to get an incorrect glyph index for certain characters in certain fonts, which affects the "Copy CMAP Subtable" function.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.5 [2009-12-31]
This update fixes a bug that causes BabelPad to crash if the tab key is pressed multiple times when the Character Map utility is open.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.6 [2010-01-02]
This update improves character search in the Character Map utility, and displays the ISO/IEC 6429 names for control characters in the Character Map utility character description (these used to be displayed, but were inadvertently dropped somewhere along the line).
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.7 [2010-01-09]
This update fixes a bug with the Join Lines function that caused it to fail to join lines under certain circumstances.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.8 [2010-06-06]
This update adds the following features :
- Adds support for the 'Standard Compression Scheme for Unicode' (SCSU), using code kindly supplied by Doug Ewell. Documents can now be opened and saved as SCSU.
- Adds conversion from Unicode text to UTF-8 hexadecimal and octal byte codes.
- Add a new Batch Replace feature that allows you to execute multiple global replacements in a single operation.
- Fixes bug in the Transcode utility that meant that long lists of characters could not be pasted into the edit boxes.
- Adds a new 'HTML' character mode for the character map edit buffer.
- Fixes a bug with rendering reserved supra-BMP ranges in Simple Rendering mode.
- Corrects some CJK radical/stroke counts.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.9 [2010-06-07]
This update fixes a bug that causes BabelPad to crash when displaying reserved character ranges under certain circumstances.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.10 [2010-06-09]
Refixes a bug whereby some of the radicals in the Han Radical Lookup Utility were displayed as the wrong character.
BabelPad Version 5.2.0.11 [2010-06-18]
Fixes a bug with the block coverage statistics in the Composite Font Mappings dialog.
BabelPad Version 6.0.0.0 BETA [2010-07-04]
Beta releases of BabelPad and BabelMap suporting Unicode 6.0 are now available for download:
- BabelPad Beta C [2010-07-04]
- BabelMap Beta C [2010-07-04]
Caveat: The Unicode properties in BabelMap/BabelPad are based on the latest versions of the Unicode 6.0 Beta data files, and although the data is unlikely to change substantially before the release of Unicode 6.0 in late September, some properties may be subject to change, and should not be relied on. However, character names and code points are fixed, and may be relied on.
As usual, please send any bug reports or feature requests to me (see my profile for my email address).
Index of BabelStone Blog Posts